1. 架构
1.1 架构
1.1.1 架构
2. 网络
2.1 网络
2.1.1 NSURLRequest
常见的请求头设置属性:
Host: 目标服务器的网络地址
Accept: 让服务端知道客户端所能接收的数据类型,如text/html
Content-Type: body中的数据类型,如application/json; charset=UTF-8
Accept-Language: 客户端的语言环境,如zh-cn
Accept-Encoding: 客户端支持的数据压缩格式,如gzip
User-Agent: 客户端的软件环境,我们可以更改该字段为自己客户端的名字,比如QQ music v1.11,比如浏览器Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/600.8.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Maxthon/4.5.2
Connection: keep-alive,该字段是从HTTP 1.1才开始有的,用来告诉服务端这是一个持久连接,“请服务端不要在发出响应后立即断开TCP连接”。关于该字段的更多解释将在后面的HTTP版本简介中展开。
Content-Length: body的长度,如果body为空则该字段值为0。该字段一般在POST请求中才会有。
NSMutableURLRequest *mulrequest = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"http"] cachePolicy:(NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalCacheData) timeoutInterval:10];
[mulrequest setHTTPMethod:@"POST"];
NSString *TWITTERFON_FORM_BOUNDARY = @"12344321";
NSString *content = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"multipart/form-data; boundary=%@",TWITTERFON_FORM_BOUNDARY];
[mulrequest setValue:content forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Type"];
NSString *boundary = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"--%@",TWITTERFON_FORM_BOUNDARY];
NSString *endBoundary = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"--%@--",TWITTERFON_FORM_BOUNDARY];
NSDictionary *param = @{@"name":@"mike"};
NSMutableString *body = [NSMutableString string];
NSArray *keys = [param allKeys];
for (NSString *key in keys) {
[body appendFormat:@"%@\r\n",boundary];
[body appendFormat:@"Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\"%@\"\r\n\r\n",key];
[body appendFormat:@"%@\r\n",[dic objectForKey:key]];
}
[body appendFormat:@"%@\r\n",boundary];
[body appendFormat:@"Content-Disposition:form-data; name=\"pic\"; filename=\"myPic.jpg\"\r\n"];
[body appendFormat:@"Cotent-Type: image/png"];
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"pic"];
NSData *imageData = UIImageJPEGRepresentation(image, 0.3);
NSMutableData *requestData = [NSMutableData data];
[requestData appendData:[body dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[requestData appendData:imageData];
[requestData appendData:[[NSString stringWithFormat:@"\r\n%@",endBoundary] dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]];
[mulrequest setValue:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%lu", [requestData length]] forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Length"];
[mulrequest setHTTPBody:requestData];
NSURLSessionConfiguration *sessionCon = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
NSURLSession *session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:sessionCon];
NSURLSessionDataTask *task = [session dataTaskWithRequest:mulrequest completionHandler:^(NSData * _Nullable data, NSURLResponse * _Nullable response, NSError * _Nullable error) {
NSLog(@"complite");
}];
[task resume];
4. 信息安全
4.1 (防止反编译、APP安全)
HTTPS配置
本地数据加密
对NSUserDefaults,sqlite存储文件数据加密,保护帐号和关键信息
URL编码加密
对程序中出现的URL进行编码加密,防止URL被静态分析。(YYKit 分类)
admin.php?act=zhongguo&tx=123 编码 admin.php%3Fact%3Dzhongguo%26tx%3D123
?=> %3F
= => %3D
% => %25
& => %26
\ => %5C
网络传输数据加密
对客户端传输数据提供加密方案,有效防止通过网络接口的拦截获取数据。
签名实现方案:
#pragma mark - HeaderAndSign
/**
设置header字段
@param parameters body中的参数
*/
- (void)setHTTPHeaderWithBodyParameters:(NSDictionary *)parameters {
NSDictionary *HTTPHeaderField = [self theHTTPHeaderFieldNoSign];
NSDictionary *unsignedParameters = [self theUnsignedParameters:parameters];
NSString *sign = [self signStringWithParameters:unsignedParameters];
[HTTPHeaderField enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(id _Nonnull key, id _Nonnull obj, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
[self.requestSerializer setValue:obj forHTTPHeaderField:key];
}];
[self.requestSerializer setValue:kSafeString(sign) forHTTPHeaderField:@"wkch-sign"];
}
/**
获取不包括sign的header参数
@return header参数
*/
- (NSDictionary *)theHTTPHeaderFieldNoSign {
NSString *uniqueId = [JGKeyChainDataManager readUUID];
if (isEmpty(uniqueId)) {
uniqueId = [JGKeyChainDataManager createUUID];
[JGKeyChainDataManager saveUUID:uniqueId];
}
NSString *version = ([[NSBundle mainBundle] infoDictionary][@"CFBundleShortVersionString"]);
NSString *timestamp = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%.f", [[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970]];
NSString *mobileAccessToken = kSafeString(kUserInfo.userInfoModel.accessToken);
NSString *uIdString = isEmpty(kUserInfo.userInfoModel.id) ? @"0" : kSafeString(kUserInfo.userInfoModel.id);
// deviceType 设备:1:安卓 2:iOS
NSDictionary *dictionary = @{
@"deviceType" : @"2",
@"uniqueId" : kSafeString(uniqueId),
@"version" : kSafeString(version),
@"app" : @"bundle-id",
@"timestamp" : kSafeString(timestamp),
@"uId" : uIdString,
@"mobileAccessToken" : kSafeString(mobileAccessToken)
};
return dictionary;
}
/**
获取未签名的所有参数
@param params 参数
@return 未签名的所有参数
*/
- (NSDictionary *)theUnsignedParameters:(NSDictionary *)params {
NSDictionary *headerDictionary = [self theHTTPHeaderFieldNoSign];
NSMutableDictionary *muDictionary = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithDictionary:headerDictionary];
if (params) {
[muDictionary addEntriesFromDictionary:params];
}
return muDictionary;
}
/**
获取加密后的sign字符串
@param parameters 所有参数
@return sign字符串
*/
- (NSString *)signStringWithParameters:(NSDictionary *)parameters {
NSStringCompareOptions comparisonOptions = (NSCaseInsensitiveSearch |
NSNumericSearch |
NSWidthInsensitiveSearch |
NSForcedOrderingSearch);
NSComparator sort = ^(NSString *obj1, NSString *obj2) {
NSRange range = NSMakeRange(0, obj1.length);
return [obj1 compare:obj2 options:comparisonOptions range:range];
};
NSArray *allKeys = parameters.allKeys;
NSArray *sortedAllKeys = [allKeys sortedArrayUsingComparator:sort];
NSMutableArray *keyValues = [[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithCapacity:sortedAllKeys.count];
for (NSString *key in sortedAllKeys) {
NSString *keyValue = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@=%@",key, parameters[key]];
[keyValues addObject:keyValue];
}
NSString *sign = [keyValues componentsJoinedByString:@"&"];
if (isEmpty(sign)) {
return @"";
}
return [sign md5Hash];
}
方法体,方法名高级混淆
对应用程序的方法名和方法体进行混淆,保证源码被逆向后无法解析代码。
程序结构混排加密
对应用程序逻辑结构进行打乱混排,保证源码可读性降到最低
借助第三方APP加固,例如:网易云易盾
4.2 加密解密
- 对称加密是最快速、最简单的一种加密方式,加密(encryption)与解密(decryption)用的是同样的密钥(secret key)。
- 非对称加密算法需要两个密钥:公开密钥(publickey)和私有密钥(privatekey)。公开密钥与私有密钥是一对,如果用公开密钥对数据进行加密,只有用对应的私有密钥才能解密;如果用私有密钥对数据进行加密,那么只有用对应的公开密钥才能解密。安全性高,但加密与解密速度慢
Base64(对称)
大致以“=”号结尾
AES(对称)
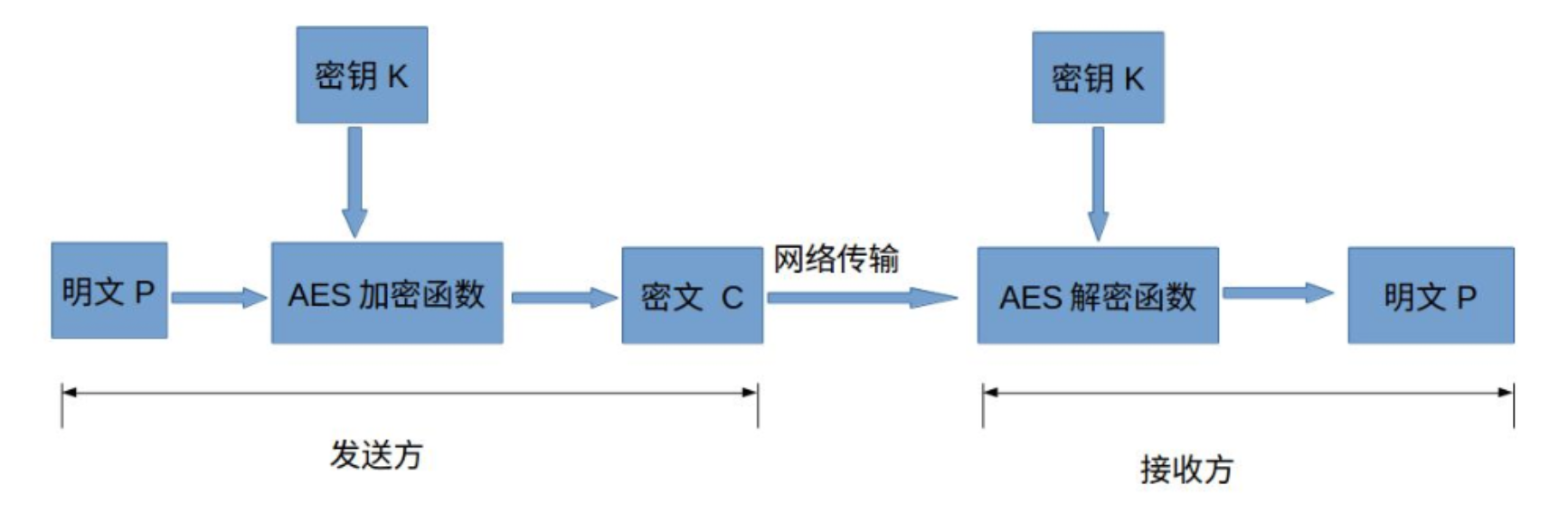
高级加密标准(英语:Advanced Encryption Standard,缩写:AES),是一种区块加密标准。这个标准用来替代原先的DES,已经被多方分析且广为全世界所使用。
那么为什么原来的DES会被取代呢,,原因就在于其使用56位密钥,比较容易被破解。而AES可以使用128、192、和256位密钥,并且用128位分组加密和解密数据,相对来说安全很多。完善的加密算法在理论上是无法破解的,除非使用穷尽法。使用穷尽法破解密钥长度在128位以上的加密数据是不现实的,仅存在理论上的可能性。统计显示,即使使用目前世界上运算速度最快的计算机,穷尽128位密钥也要花上几十亿年的时间,更不用说去破解采用256位密钥长度的AES算法了。
目前世界上还有组织在研究如何攻破AES这堵坚厚的墙,但是因为破解时间太长,AES得到保障,但是所用的时间不断缩小。随着计算机计算速度的增快,新算法的出现,AES遭到的攻击只会越来越猛烈,不会停止的。
AES现在广泛用于金融财务、在线交易、无线通信、数字存储等领域,经受了最严格的考验,但说不定哪天就会步DES的后尘。
MD5(非对称)
历史版本有MD2、MD4、MD5,消息摘要算法各个版本间的结果是不一样的。MD5是目前广泛使用的版本,不过其安全性多年前就开始被质疑(碰撞算法)。于是在2008年提出了MD6算法,其后MD6历经数次改进,目前还是试行方案阶段,未被正式使用。
消息摘要算法,32位=16个2位16进制。
SHA(非对称)
安全散列算法,包括SHA-1、SHA-224、SHA-256、SHA-384,和SHA-512,和MD5类似,但安全性要高于MD5,运算性能有低于MD5。
RSA(非对称)
- 加密/解密和签名/验签过程
A->B:
- A提取消息m的消息摘要h(m),并使用自己的私钥对摘要h(m)进行加密,生成签名s
- A将签名s和消息m一起,使用B的公钥进行加密,生成密文c,发送给B
B:
- B接收到密文c,使用自己的私钥解密c得到明文m和数字签名s
- B使用A的公钥解密数字签名s解密得到H(m)
- B使用相同的方法提取消息m的消息摘要h(m)
- B比较两个消息摘要。相同则验证成功;不同则验证失败
例:PHP后台,邀请码,对用户敏感信息进行加密
5. 语法
5.1 const常量与define宏定义
5.1.1 const与#define的区别
#define RADIUS 100;
const float RADIUS = 100;
- 编译器处理方式不同
- define宏是在预处理阶段展开。
- const常量是编译运行阶段使用。
- 类型和安全检查不同
- define宏没有类型,不做任何类型检查,仅仅是展开。
- const常量有具体的类型,在编译阶段会执行类型检查。
- 存储方式不同
- define宏仅仅是展开,有多少地方使用,就展开多少次,不会分配内存。(宏定义不分配内存,变量定义分配内存。)
- const常量会在内存中分配(可以是堆中也可以是栈中)。
const可以节省空间,避免不必要的内存分配.‘#define PI 3.14159 //常量宏
const doulbe Pi=3.14159; //此时并未将Pi放入ROM中
double i=Pi; //此时为Pi分配内存,以后不再分配!
double I=PI; //编译期间进行宏替换,分配内存
double j=Pi; //没有内存分配
double J=PI; //再进行宏替换,又一次分配内存
const定义常量从汇编的角度来看,只是给出了对应的内存地址,而不是象#define一样给出的是立即数,所以,const定义的常量在程序运行过程中只有一份拷贝(因为是全局的只读变量,存在静态区),而#define定义的常量在内存中有若干个拷贝。- 提高了效率
编译器通常不为普通const常量分配存储空间,而是将它们保存在符号表中,这使得它成为一个编译期间的常量,没有了存储与读内存的操作,使得它的效率也很高。
- 宏替换只作替换,不做计算,不做表达式求解
- 宏预编译时就替换了,程序运行时,并不分配内存。
5.1.2 const与#define的比较
C++ 语言可以用const来定义常量,也可以用 #define来定义常量。但是前者比后者有更多的优点:
- const常量有数据类型,而宏常量没有数据类型。编译器可以对前者进行类型安全检查。而对后者只进行字符替换,没有类型安全检查,并且在字符替换可能会产生意料不到的错误(边际效应)。
- 有些集成化的调试工具可以对const常量进行调试,但是不能对宏常量进行调试。
5.2 数组(字典)中添加弱引用;NSPointerArray(NSArray)、NSHashTable(NSSet)、NSMapTable(NSDictionary)
自定义弱引用:
- 通过NSValue的方法
+ valueWithNonretainedObject:和nonretainedObjectValue存取对象
- (nullable id)objectForKey:(id<NSCopying>)aKey {
NSValue *value = [self objectForKey:aKey];
return value.nonretainedObjectValue;
}
- (void)fm_setObject:(id)anObject forKey:(id <NSCopying>)aKey {
NSValue *value = [NSValue valueWithNonretainedObject:anObject];
[self setObject:value forKey:aKey];
}
- (void)fm_setDictionary:(NSDictionary *)otherDictionary {
[otherDictionary enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(id _Nonnull key,
id _Nonnull obj,
BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
[self fm_setObject:obj forKey:key];
}];
}
- 用block封装与解封
typedef id (^WeakReference)(void);
WeakReference makeWeakReference(id object) {
__weak id weakref = object;
return ^{
return weakref;
};
}
id weakReferenceNonretainedObjectValue(WeakReference ref) {
return ref ? ref() : nil;
}
- (void)weak_setObject:(id)anObject forKey:(NSString *)aKey {
[self setObject:makeWeakReference(anObject) forKey:aKey];
}
- (void)weak_setObjectWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dic {
for (NSString *key in dic.allKeys) {
[self setObject:makeWeakReference(dic[key]) forKey:key];
}
}
- (id)weak_getObjectForKey:(NSString *)key {
return weakReferenceNonretainedObjectValue(self[key]);
}
- 使用NSProxy 的子类,像YYKit 这套框架就是用的这种方法
@interface YYWeakProxy : NSProxy
/**
The proxy target.
*/
@property (nullable, nonatomic, weak, readonly) id target;
/**
Creates a new weak proxy for target.
@param target Target object.
@return A new proxy object.
*/
- (instancetype)initWithTarget:(id)target;
+ (instancetype)proxyWithTarget:(id)target;
@end
@implementation YYWeakProxy
- (instancetype)initWithTarget:(id)target {
_target = target;
return self;
}
+ (instancetype)proxyWithTarget:(id)target {
return [[YYWeakProxy alloc] initWithTarget:target];
}
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)selector {
return _target;
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation {
void *null = NULL;
[invocation setReturnValue:&null];
}
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)selector {
return [NSObject instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:@selector(init)];
}
- (BOOL)respondsToSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
return [_target respondsToSelector:aSelector];
}
//...
@end
@implementation MyView {
NSTimer *_timer;
}
- (void)initTimer {
YYWeakProxy *proxy = [YYWeakProxy proxyWithTarget:self];
_timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:0.1
target:proxy
selector:@selector(tick:)
userInfo:nil
repeats:YES];
}
- (void)tick:(NSTimer *)timer {...}
@end
5.3 @private @protected @public @package
@private 私有的,也就是只有自己有,别人谁都不可用,哪怕亲如自己的孩子。
@protected 受保护的,他自己可以用,自己的孩子也是可以共享的。
@public 公共的,谁都可以用,只要你有这个类的对象,就可以拿到public下的变量。
@package 这个主要是用于框架类。
5.5 valueForKey与valueForKeyPath
不同点:valueForKeyPath的使用更加广泛,功能也更加强大:
- 1.如:sum/average/max/min
NSArray *array1 = @[@1, @3, @5, @7, @9,@11, @13];
NSInteger sum = [[array2 valueForKeyPath:@"@sum.floatValue"] integerValue];
NSInteger avg = [[array2 valueForKeyPath:@"@avg.floatValue"] integerValue];
NSInteger max = [[array2 valueForKeyPath:@"@max.floatValue"] integerValue];
NSInteger min = [[array2 valueForKeyPath:@"@min.floatValue"] integerValue];
- 2.删除数组中重复的数据
NSArray *array2 = @[@1, @3, @5, @7, @9,@11, @13, @7, @9,@11];
NSLog(@"deleteKeyPath---%@",[array2 valueForKeyPath:@"@distinctUnionOfObjects.self"]);
- 3.深层次取字典中出子属性
valueForKeyPath:可以深层次取到子属性,不管隐藏的多深
valueForKey:无法取到深层次子属性
NSDictionary *dic = @{@"dic1":@{@"dic2":@{@"name":@"zhangsanfeng",@"info":@{@"age":@"13"}}}};
NSLog(@"KeyPath---%@",[dic valueForKeyPath:@"dic1.dic2.info.age"]);///可以深层次的取到子层级属性
NSLog(@"Key---%@",[dic valueForKey:@"dic1.dic2.info.age"]);///无法深层次取到子层级属性
相同点:
- 1.快速找到字典数组中key所对应的值
NSArray *dicArray = @[
@{@"company":@"baidu",@"person":@{@"name":@"zhangsanfeng"}},
@{@"position":@"chengdu"}];
NSLog(@"keyPath---%@", [dicArray valueForKeyPath:@"company"]);
NSLog(@"key-- -%@", [dicArray valueForKey:@"company"]);
- 2.大小写字母转换
NSArray *arra3 = @[@"name",@"w",@"b",@"h",@"g",@"d",@"r",@"p"];
///打印由小写字母--->大写字母
NSLog(@"KeyPath---%@",[array valueForKeyPath:@"uppercaseString"]);
NSArray *newArray = [array valueForKey:@"uppercaseString"];
NSLog(@"newArray---%@",newArray);